To Learn Data Structures and Algorithms

The term DSA stands for Data Structures and Algorithms, in the context of Computer Science. Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA)
What is DSA?
DSA is defined as a combination of two separate yet interrelated topics – Data Structure and Algorithms. DSA is one of the most important skills that every computer science student must-have. It is often seen that people with good knowledge of these technologies are better programmers than others and thus, crack the interviews of almost every tech giant.
- What is Data Structure?
- What are Algorithms?
- How to learn Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) from scratch
-
- Learn Data Structure
- Array
- String
- Linked List
- Matrix/Grid
- Stack
- Queue
- Heap
- Hash
- Tree Data Structures
- Binary Tree
- Binary Search Tree
- Other Tree Data Structures
- Graph Data Structure
- Learn Data Structure
-
- Learn Algorithms
- Searching Algorithm
- Sorting Algorithm
- Divide and Conquer Algorithm
- Greedy Algorithms
- Recursion
- Backtracking Algorithm
- Dynamic Programming
- Pattern Searching
- Mathematical Algorithms
- Geometric Algorithms
- Bitwise Algorithms
- Randomized Algorithms
- Branch and Bound Algorithm
- Practice problems on DSA
- Learn Algorithms
What is the target audience?
- You might be thinking, all of the above – and that is fine. But as a complete beginner learning Unreal Engine 4.
- The rendering system in Unreal Engine 4 is an all-new, DirectX 11 pipeline that includes deferred shading.
Learning a new game engine as a complete beginner is very intimidating. There are a lot of tutorials, documentation and advice already out but how do you start and proceed with learning Unreal Engine 4 is unclear. You get pulled into many different directions and end up confused and overwhelmed. I have spent a lot of time deconstructing what it takes to learn a game engine from scratch. What it is that you should focus on first and what you should avoid until later.
What is Data Structure?
A data structure is defined as a particular way of storing and organizing data in our devices to use the data efficiently and effectively. The main idea behind using data structures is to minimize the time and space complexities. An efficient data structure takes minimum memory space and requires minimum time to execute the data.
What is Algorithm?
Algorithm is defined as a process or set of well-defined instructions that are typically used to solve a particular group of problems or perform a specific type of calculation. To explain in simpler terms, it is a set of operations performed in a step-by-step manner to execute a task.
How to start learning DSA?
The first and foremost thing is dividing the total procedure into little pieces which need to be done sequentially.
The complete process to learn DSA from scratch can be broken into 4 parts:
- Learn about Time and Space complexities
- Learn the basics of individual Data Structures
- Learn the basics of Algorithms
- Practice Problems on DSA
1. Learn about Complexities
Here comes one of the interesting and important topics. The primary motive to use DSA is to solve a problem effectively and efficiently. How can you decide if a program written by you is efficient or not? This is measured by complexities. Complexity is of two types:
- Time Complexity: Time complexity is used to measure the amount of time required to execute the code.
- Space Complexity: Space complexity means the amount of space required to execute successfully the functionalities of the code.
You will also come across the term Auxiliary Space very commonly in DSA, which refers to the extra space used in the program other than the input data structure.
Both of the above complexities are measured with respect to the input parameters. But here arises a problem. The time required for executing a code depends on several factors, such as:
- The number of operations performed in the program,
- The speed of the device, and also
- The speed of data transfer if being executed on an online platform.
So how can we determine which one is efficient? The answer is the use of asymptotic notation.
Asymptotic notation is a mathematical tool that calculates the required time in terms of input size and does not require the execution of the code.
It neglects the system-dependent constants and is related to only the number of modular operations being performed in the whole program. The following 3 asymptotic notations are mostly used to represent the time complexity of algorithms:
- Big-O Notation (Ο) – Big-O notation specifically describes the worst-case scenario.
- Omega Notation (Ω) – Omega(Ω) notation specifically describes the best-case scenario.
- Theta Notation (θ) – This notation represents the average complexity of an algorithm.
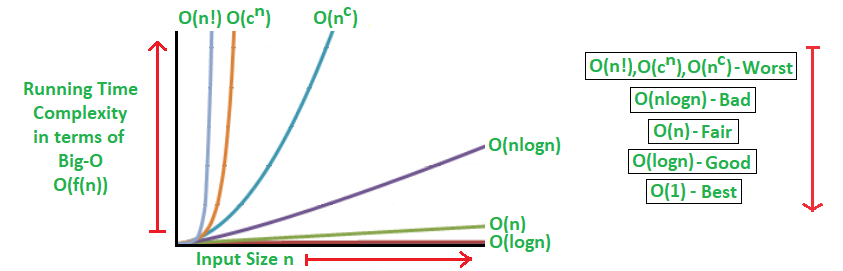
Rate of Growth of Algorithms
The most used notation in the analysis of a code is the Big O Notation which gives an upper bound of the running time of the code (or the amount of memory used in terms of input size).
To learn about complexity analysis in detail, you can refer to our complete set of articles on the Analysis of Algorithms.
2. Learn Data Structures
Here comes the most crucial and the most awaited stage of the roadmap for learning data structure and algorithm – the stage where you start learning about DSA. The topic of DSA consists of two parts:
- Data Structures
- Algorithms
Though they are two different things, they are highly interrelated, and it is very important to follow the right track to learn them most efficiently. If you are confused about which one to learn first, we recommend you to go through our detailed analysis on the topic: What should I learn first- Data Structures or Algorithms?
Here we have followed the flow of learning a data structure and then the most related and important algorithms used by that data structure.
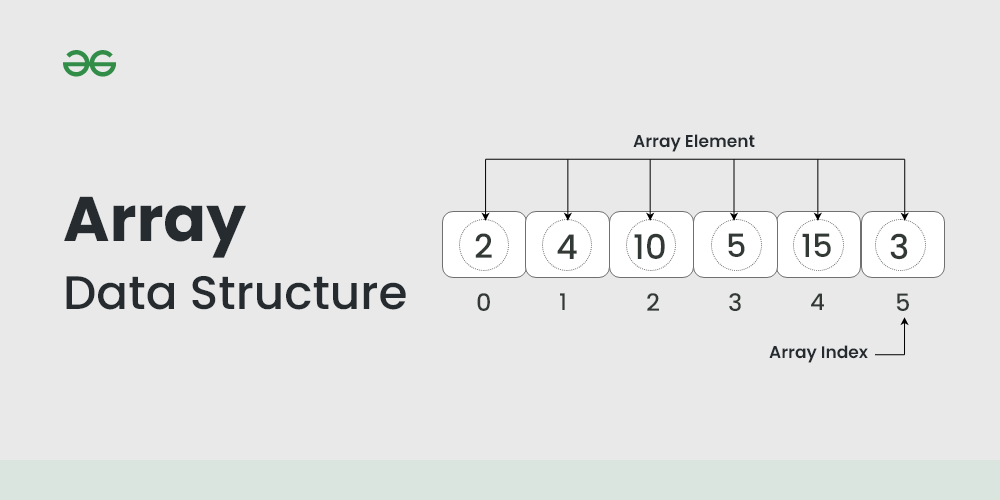
1. Array
The most basic yet important data structure is the array. It is a linear data structure. An array is a collection of homogeneous data types where the elements are allocated contiguous memory. Because of the contiguous allocation of memory, any element of an array can be accessed in constant time. Each array element has a corresponding index number.
To learn more about arrays, refer to the article “Introduction to Arrays“.
Here are some topics about array which you must learn:
- Reverse Array – Reverse an array means shifting the elements of an array in a reverse manner i.e., the last element becomes the first element, second last element becomes the second element, and so on.
- Rotation of Array – Rotation of array means shifting the elements of an array in a circular manner i.e., in the case of right circular shift the last element becomes the first element, and all other element moves one point to the right.
- Rearranging an array – Rearrangement of array elements suggests the changing of an initial order of elements following some conditions or operations.
- Range queries in the array – Often you need to perform operations on a range of elements. These functions are known as range queries.
- Multidimensional array – These are arrays having more than one dimension. The most used one is the 2-dimensional array, commonly known as a matrix.
- Kadane’s algorithm
- Dutch national flag algorithm
Related posts:
2. String
A string is also a type of array. It can be interpreted as an array of characters. But it has some special characteristics like the last character of a string is a null character to denote the end of the string. Also, there are some unique operations, like concatenation which concatenates two strings into one.
Here we are providing you with some must-know concepts of string:
- Subsequence and substring – A subsequence is a sequence that can be derived from a string deleting one or more elements. A substring is a contiguous segment of the string.
- Reverse and rotation in a string – Reverse operation is interchanging the position of characters of a string such that the first becomes the last, the second becomes the second last, and so on.
- Binary String – A binary string is a string made up of only two types of characters.
- Palindrome – A palindrome string is a string in which the elements at the same distance from the center of the string are the same.
- Lexicographic pattern – Lexicographical pattern is the pattern based on the ASCII value or can be said in dictionary order.
- Pattern searching – Pattern searching is searching a given pattern in the string. It is an advanced topic of string.
Related posts:
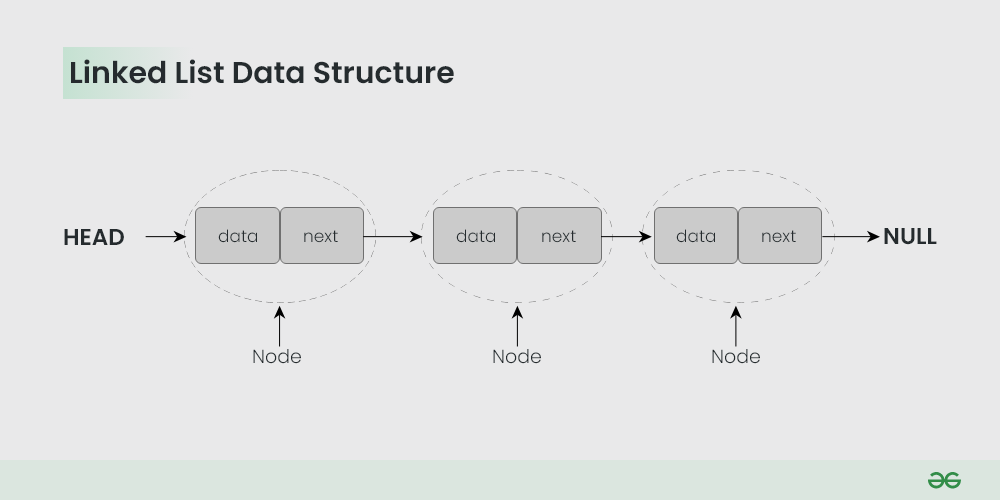
3. Linked Lists
As the above data structures, the linked list is also a linear data structure. But Linked List is different from Array in its configuration. It is not allocated to contiguous memory locations. Instead, each node of the linked list is allocated to some random memory space and the previous node maintains a pointer that points to this node. So no direct memory access of any node is possible and it is also dynamic i.e., the size of the linked list can be adjusted at any time. To learn more about linked lists refer to the article “Introduction to Linked List“.
The topics which you must want to cover are:
- Singly Linked List – In this, each node of the linked list points only to its next node.
- Circular Linked List – This is the type of linked list where the last node points back to the head of the linked list.
- Doubly Linked List – In this case, each node of the linked list holds two pointers, one point to the next node and the other points to the previous node.
Related posts:
- Introduction to Linked Lists
- Practice Problems on Linked Lists
4. Matrix/Grid
A matrix represents a collection of numbers arranged in an order of rows and columns. It is necessary to enclose the elements of a matrix in parentheses or brackets.
For example:
A matrix with 9 elements is shown below.
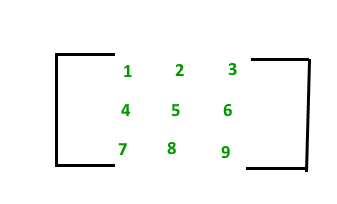
This Matrix M has 3 rows and 3 columns. Each element of matrix M can be referred to by its row and column number. For example, M[2][3] = 6.
Related posts:
- Introduction to Matrix/Grid
- Practice Problems on Matrix/Grid
5. Stack
Now you should move to some more complex data structures, such as Stack and Queue.
Stack is a linear data structure which follows a particular order in which the operations are performed. The order may be LIFO(Last In First Out) or FILO(First In Last Out).
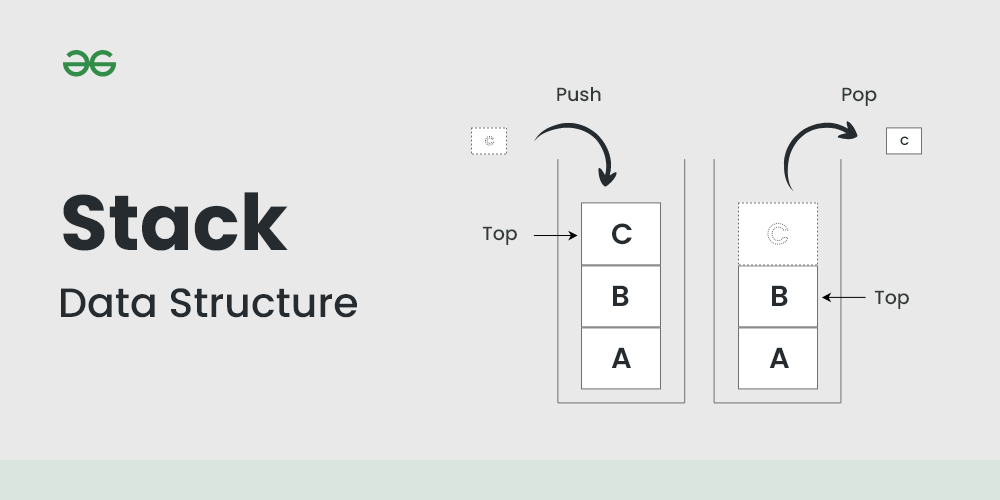
Stack Data Structure
The reason why Stack is considered a complex data structure is that it uses other data structures for implementation, such as Arrays, Linked lists, etc. based on the characteristics and features of Stack data structure.
Related posts:
- Introduction to Stack
- Practice Problems on Stack
6. Queue
Another data structure that is similar to Stack, yet different in its characteristics, is Queue.
A Queue is a linear structure which follows First In First Out (FIFO) approach in its individual operations.
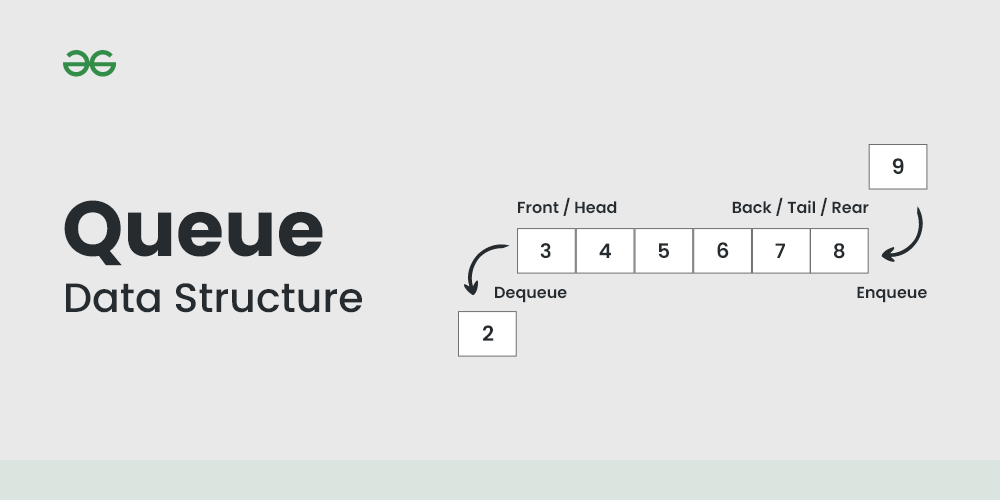
Queue Data Structure
A queue can be of different types like
- Circular queue – In a circular queue the last element is connected to the first element of the queue
- Double-ended queue (or known as deque) – A double-ended queue is a special type of queue where one can perform the operations from both ends of the queue.
- Priority queue – It is a special type of queue where the elements are arranged as per their priority. A low priority element is dequeued after a high priority element.
Related posts:
- Introduction to Queue
- Practice Problems on Queue
7. Heap
A Heap is a special Tree-based Data Structure in which the tree is a complete binary tree.
Types of heaps:
Generally, heaps are of two types.
Max-Heap:
In this heap, the value of the root node must be the greatest among all its child nodes and the same thing must be done for its left and right sub-tree also.
Min-Heap:
In this heap, the value of the root node must be the smallest among all its child nodes and the same thing must be done for its left ans right sub-tree also.
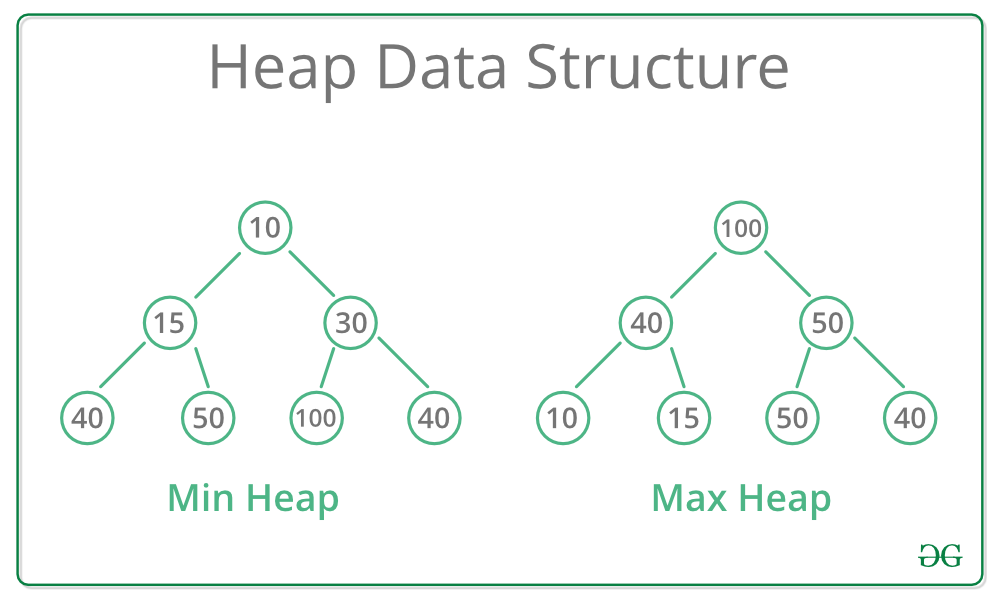
Types of Heap Data Structure
Related posts:
8. Hash
Hashing refers to the process of generating a fixed-size output from an input of variable size using the mathematical formulas known as hash functions. This technique determines an index or location for the storage of an item in a data structure.
Related posts:
9. Tree Data Structures
After having the basics covered about the linear data structure, now it is time to take a step forward to learn about the non-linear data structures. The first non-linear data structure you should learn is the tree.
Tree data structure is similar to a tree we see in nature but it is upside down. It also has a root and leaves. The root is the first node of the tree and the leaves are the ones at the bottom-most level. The special characteristic of a tree is that there is only one path to go from any of its nodes to any other node.
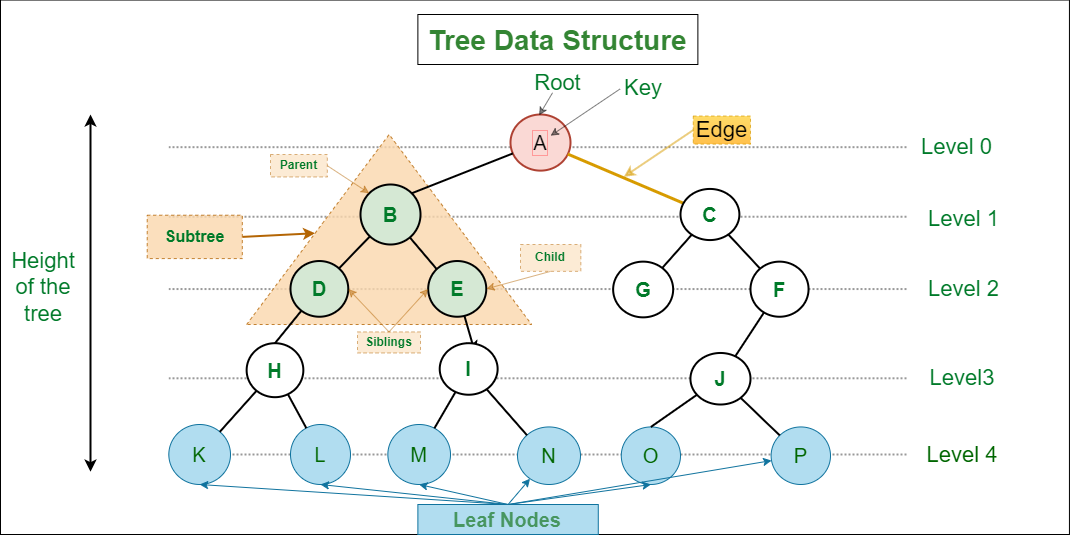
Tree Data Structure
Based on the maximum number of children of a node of the tree it can be –
- Binary tree – This is a special type of tree where each node can have a maximum of 2 children.
- Ternary tree – This is a special type of tree where each node can have a maximum of 3 children.
- N-ary tree – In this type of tree, a node can have at most N children.
Based on the configuration of nodes there are also several classifications. Some of them are:
- Complete Binary Tree – In this type of binary tree all the levels are filled except maybe for the last level. But the last level elements are filled as left as possible.
- Perfect Binary Tree – A perfect binary tree has all the levels filled
- Binary Search Tree – A binary search tree is a special type of binary tree where the smaller node is put to the left of a node and a higher value node is put to the right of a node
- Ternary Search Tree – It is similar to a binary search tree, except for the fact that here one element can have at most 3 children.
Related posts:
10. Graph Data Structure
Another important non-linear data structure is the graph. It is similar to the Tree data structure, with the difference that there is no particular root or leaf node, and it can be traversed in any order.
A Graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of a finite set of vertices(or nodes) and a set of edges that connect a pair of nodes.
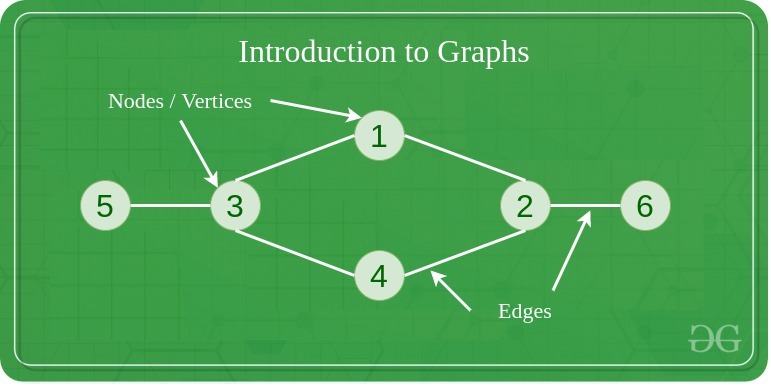
Graph Data Structure
Each edge shows a connection between a pair of nodes. This data structure helps solve many real-life problems. Based on the orientation of the edges and the nodes there are various types of graphs.
Here are some must to know concepts of graphs:
- Types of graphs – There are different types of graphs based on connectivity or weights of nodes.
- Introduction to BFS and DFS – These are the algorithms for traversing through a graph
- Cycles in a graph – Cycles are a series of connections following which we will be moving in a loop.
- Topological sorting in the graph
- Minimum Spanning tree in graph
Related posts:
3. Learn Algorithms
Once you have cleared the concepts of Data Structures, now its time to start your journey through the Algorithms. Based on the type of nature and usage, the Algorithms are grouped together into several categories, as shown below:
1. Searching Algorithm
Now we have learned about some linear data structures and is time to learn about some basic and most used algorithms which are hugely used in these types of data structures. One such algorithm is the searching algorithm.
Searching algorithms are used to find a specific element in an array, string, linked list, or some other data structure.
The most common searching algorithms are:
- Linear Search – In this searching algorithm, we check for the element iteratively from one end to the other.
- Binary Search – In this type of searching algorithm, we break the data structure into two equal parts and try to decide in which half we need to find for the element.
- Ternary Search – In this case, the array is divided into three parts, and based on the values at partitioning positions we decide the segment where we need to find the required element.
Besides these, there are other searching algorithms also like
2. Sorting Algorithm
Here is one other most used algorithm. Often we need to arrange or sort data as per a specific condition. The sorting algorithm is the one that is used in these cases. Based on conditions we can sort a set of homogeneous data in order like sorting an array in increasing or decreasing order.
Sorting Algorithm is used to rearrange a given array or list elements according to a comparison operator on the elements. The comparison operator is used to decide the new order of element in the respective data structure.
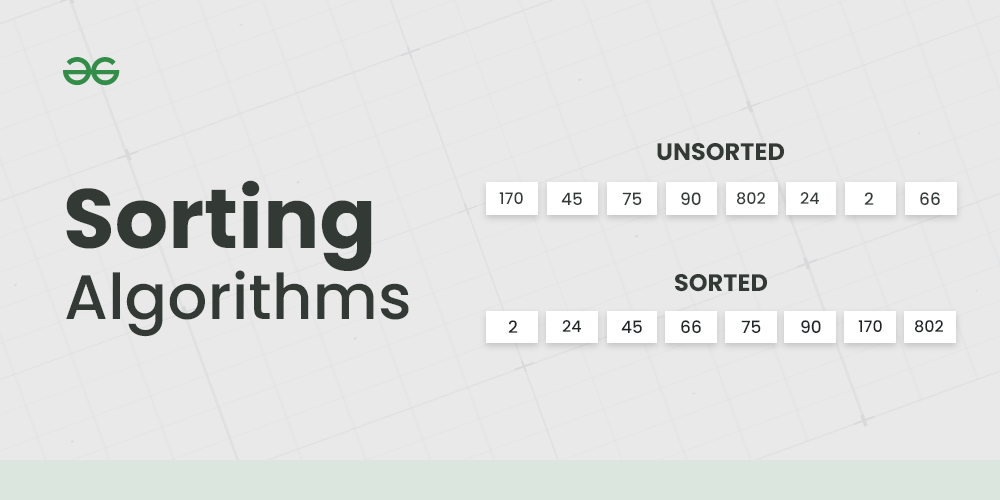
An example to show Sorting
There are a lot of different types of sorting algorithms. Some widely used algorithms are:
There are several other sorting algorithms also and they are beneficial in different cases. You can learn about them and more in our dedicated article on Sorting algorithms.
3. Divide and Conquer Algorithm
This is one interesting and important algorithm to be learned in your path of programming. As the name suggests, it breaks the problem into parts, then solves each part and after that again merges the solved subtasks to get the actual problem solved.
Divide and Conquer is an algorithmic paradigm. A typical Divide and Conquer algorithm solves a problem using following three steps.
- Divide: Break the given problem into subproblems of same type.
- Conquer: Recursively solve these subproblems
- Combine: Appropriately combine the answers
This is the primary technique mentioned in the two sorting algorithms Merge Sort and Quick Sort which are mentioned earlier. To learn more about the technique, the cases where it is used, and its implementation and solve some interesting problems, please refer to the dedicated article Divide and Conquer Algorithm.
4. Greedy Algorithms
As the name suggests, this algorithm builds up the solution one piece at a time and chooses the next piece which gives the most obvious and immediate benefit i.e., which is the most optimal choice at that moment. So the problems where choosing locally optimal also leads to the global solutions are best fit for Greedy.
For example, consider the Fractional Knapsack Problem. The local optimal strategy is to choose the item that has maximum value vs weight ratio. This strategy also leads to a globally optimal solution because we are allowed to take fractions of an item.

Fractional Knapsack Problem
Here is how you can get started with the Greedy algorithm with the help of relevant sub-topics:
- Standard greedy algorithms
- Greedy algorithms in graphs
- Greedy Algorithms in Operating Systems
- Greedy algorithms in array
- Approximate greedy algorithms for NP-complete problems
5. Recursion
Recursion is one of the most important algorithms which uses the concept of code reusability and repeated usage of the same piece of code.
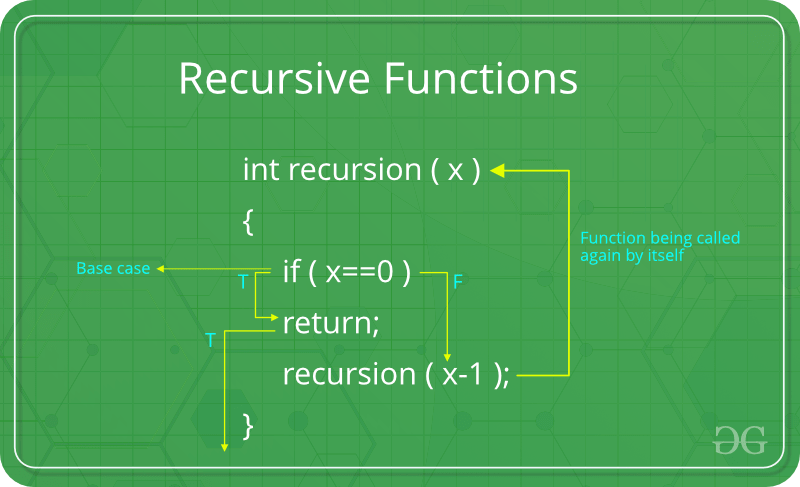
Recursion
The point which makes Recursion one of the most used algorithms is that it forms the base for many other algorithms such as:
In Recursion, you can follow the below articles/links to get the most out of it:
6. Backtracking Algorithm
As mentioned earlier, the Backtracking algorithm is derived from the Recursion algorithm, with the option to revert if a recursive solution fails, i.e. in case a solution fails, the program traces back to the moment where it failed and builds on another solution. So basically it tries out all the possible solutions and finds the correct one.
Backtracking is an algorithmic technique for solving problems recursively by trying to build a solution incrementally, one piece at a time, removing those solutions that fail to satisfy the constraints of the problem at any point of time
Some important and most common problems of backtracking algorithms, that you must solve before moving ahead, are:
- Knight’s tour problem
- Rat in a maze
- N-Queen problem
- Subset sum problem
- m-coloring problem
- Hamiltonian cycle
- Sudoku
7. Dynamic Programming
Another crucial algorithm is dynamic programming. Dynamic Programming is mainly an optimization over plain recursion. Wherever we see a recursive solution that has repeated calls for the same inputs, we can optimize it using Dynamic Programming.
The main concept of the Dynamic Programming algorithm is to use the previously calculated result to avoid repeated calculations of the same subtask which helps in reducing the time complexity.
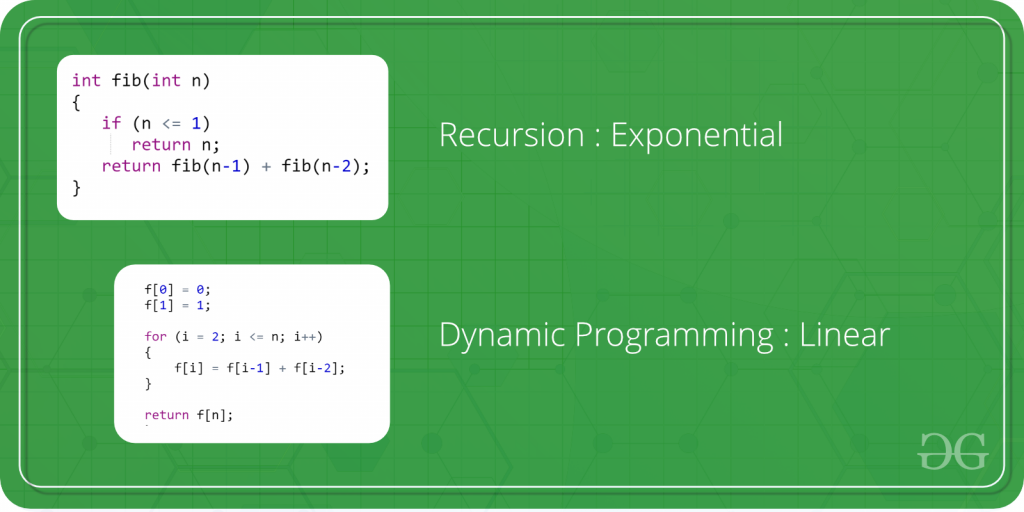
Dynamic Programming
To learn more about dynamic programming and practice some interesting problems related to it, refer to the following articles:
- Tabulation vs Memoization
- Optimal Substructure Property
- Overlapping Subproblems Property
- How to solve a Dynamic Programming Problem?
- Bitmasking and Dynamic Programming | Set 1
- Bitmasking and Dynamic Programming | Set-2 (TSP)
- Digit DP | Introduction
8. Pattern Searching
The Pattern Searching algorithms are sometimes also referred to as String Searching Algorithms and are considered as a part of the String algorithms. These algorithms are useful in the case of searching a string within another string.
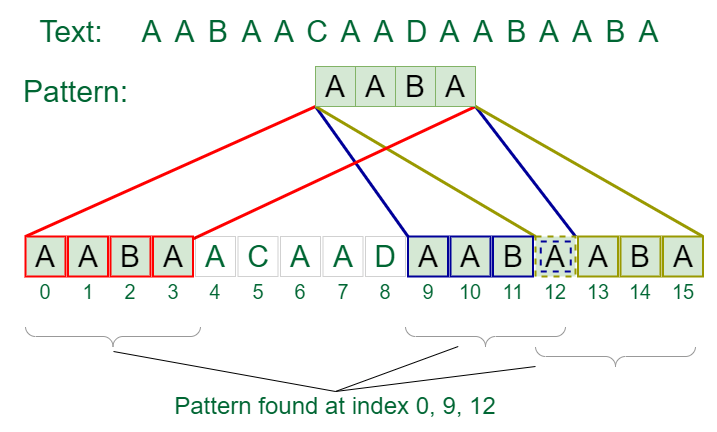
9. Mathematical Algorithms
These algorithms are designed to solve Mathematical and Number Theory problems. They requires in-depth knowledge of different mathematical concepts like
- GCD and LCM
- Prime Factorization and Divisors
- Fibonacci Numbers
- Catalan Numbers
- Modular Arithmetic
- Euler Totient Function
- nCr Computations
- Set Theory
- Factorial
- Prime numbers and Primality Tests
- Sieve Algorithms, etc.
10. Geometric Algorithms
These algorithms are designed to solve Geometric Problems. They requires in-depth knowledge of different mathematical concepts like:
- Lines
- Triangle
- Rectangle
- Square
- Circle
- 3D Objects
- Quadilateral
- Polygon & Convex Hull
For Example: Comparing Slopes of two lines, Finding Equation of a plane etc.
11. Bitwise Algorithms
The Bitwise Algorithms is used to perform operations at the bit-level or to manipulate bits in different ways. The bitwise operations are found to be much faster and are sometimes used to improve the efficiency of a program.
For example: To check if a number is even or odd. This can be easily done by using Bitwise-AND(&) operator. If the last bit of the operator is set than it is ODD otherwise it is EVEN. Therefore, if num & 1 not equals to zero than num is ODD otherwise it is EVEN.
12. Randomized Algorithms
An algorithm that uses random numbers to decide what to do next anywhere in its logic is called Randomized Algorithm. For example, in Randomized Quick Sort, we use a random number to pick the next pivot (or we randomly shuffle the array). Typically, this randomness is used to reduce time complexity or space complexity in other standard algorithms.
13. Branch and Bound Algorithm
Branch and bound is an algorithm design paradigm which is generally used for solving combinatorial optimization problems. These problems are typically exponential in terms of time complexity and may require exploring all possible permutations in worst case. The Branch and Bound Algorithm technique solves these problems relatively quickly.
4. Practice Problems on Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA)
For practicing problems on individual data structures and algorithms, you can use the following links:
- Practice problems on Arrays
- Practice problems on Strings
- Practice problems on Linked Lists
- Practice problems on Searching algorithm
- Practice problems on Sorting algorithm
- Practice problems on Divide And Conquer algorithm
- Practice problems on Stack
- Practice problems on Queue
- Practice problems on Tree
- Practice problems on Graph
- Practice problems on Greedy algorithm
- Practice problems on Recursion algorithm
- Practice problems on Backtracking algorithm
- Practice problems on Dynamic Programming algorithm
Apart from these, there are many other practice problems that you can refer based on their respective difficulties:
You can also try to solve the most asked interview questions based on the list curated by us at:
- Must-Do Coding Questions for Companies
- Top 50 Array Coding Problems for Interviews
- Top 50 String Coding Problems for Interviews
- Top 50 Tree Coding Problems for Interviews
- Top 50 Dynamic Programming Coding Problems for Interviews
You can also try our curated lists of problems from below articles:
- SDE SHEET – A Complete Guide for SDE Preparation
- DSA Sheet by Love Babbar
If you like GeeksforGeeks and would like to contribute, you can also write an article and mail your article to contribute@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks.
Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above
Starting Course
After Intro
Productivity Hacks to Get More Done in 2018
— 28 February 2017
- Facebook News Feed Eradicator (free chrome extension) Stay focused by removing your Facebook newsfeed and replacing it with an inspirational quote. Disable the tool anytime you want to see what friends are up to!
- Hide My Inbox (free chrome extension for Gmail) Stay focused by hiding your inbox. Click "show your inbox" at a scheduled time and batch processs everything one go.
- Habitica (free mobile + web app) Gamify your to do list. Treat your life like a game and earn gold goins for getting stuff done!