CPP

Learn C++ programming language
Question And Answers in Oops
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION IN OOPs(object oriented programming)
Content of C++
Introduction to C++
In this introduction to C++
C++ basic concepts
What is C++?
Popular programming languages in use?
Is C++ best programming language?
Who uses C++?
Five Basic Concepts of C++
Use of C++ Programming Language
what is C++?
C++ is a general-purpose, object-oriented programming language. It was created by Bjarne Stroustrup at Bell Labs circa 1980. C++ is very similar to C (invented by Dennis Ritchie in the early 1970s). C++ is so compatible with C that it will probably compile over 99% of C programs without changing a line of source code. Though C++ is a lot of well-structured and safer language than C as it OOPs based.
Some computer languages are written for a specific purpose. Like, Java was initially devised to control toasters and some other electronics. C was developed for programming OS. Pascal was conceptualized to teach proper programming techniques. But C++ is a general-purpose language. It well deserves the widely acknowledged nickname “Swiss Pocket Knife of Languages.”
Popular programming languages in use?
Popular languages that are mainly in use are Java, C++, Python, and C.
Lower level languages like
Assembly Language
C
C++
These languages force the programmer to think more about the problem in computer programming terms and its implementations, instead of the business logic.
Is C++ best programming language?
The answer depends on perspective and requirements. Some tasks can be done in C++, though not very quickly. For example, designing GUI screens for applications.
Other languages like Visual Basic, Python have GUI design elements built into them. Therefore, they are better suited for GUI type of task.
Some of the scripting languages that provide extra programmability to applications. Such as MS Word and even photoshop tend to be variants of Basic, not C++.
C++ is still used widely, and the most famous software have their backbone in C++.
Who uses C++?
Some of today’s most visible used systems have their critical parts written in C++.
Examples are Amadeus (airline ticketing)
Bloomberg (financial formation),
Amazon (Web commerce), Google (Web search)
Facebook (social media)
Many programming languages depend on C++’s performance and reliability in their implementation. Examples include:
Java Virtual Machines
JavaScript interpreters (e.g., Google’s V8)
Browsers (e.g., Internet Explorer, Mozilla’s Firefox, Apple’s Safari, and Google’s Chrome)
Application and Web frameworks (e.g., Microsoft’s .NET Web services framework).
Applications that involve local and wide area networks, user interaction, numeric, graphics, and database access highly depend on C++ language.
Five Basic Concepts of C++
Here are five basic C++ concepts:
C++ Variables
- Variables are the backbone of any programming language.
- A variable is merely a way to store some information for later use.
- We can retrieve this value or data by referring to a “word” that will describe this information.
- Once declared and defined they may be used many times within the scope in which they were declared.
C++ Control Structures
- When a program runs, the code is read by the compiler line by line (from top to bottom, and for the most part left to right).
- This is known as “code flow.“
- When the code is being read from top to bottom, it may encounter a point where it needs to make a decision.
- Based on the decision, the program may jump to a different part of the code.
- It may even make the compiler re-run a specific piece again, or just skip a bunch of code.
- You could think of this process like if you were to choose from different courses from Guru99.
- You decide, click a link and skip a few pages. In the same way, a computer program has a set of strict rules to decide the flow of program execution.
C++ DataStructure
With the help of data structures, you can organize data in a particular way so that it can be used effectively. There are several ways to organize the data in memory.
Let me tell you that it is not a programming language, it is a set of algorithms which one can use to structure data into memory in any programming language.
Below, we stored a list of items using the array data structure.
Data Types C++
It is just a group of similar data under a single name. Data types that are similar share similar characteristics and behave in a similar way.
For example, if you want to store the address of a person or house then you should use ‘string’ data type.
Data types are categorized into two broad categories:-
1. Primitive Data Type:- These are pre-defined data types. It is also known as fundamental data types. Example:- int, float, double, char, string etc.
2. Non-Primitive Data Type:- These are user-defined data types. Example:- array, structures, unions, structures, linked lists etc.
Types of Data Structures in C++
In C++, data structures are further categorized into 3 types.
1. Simple Data Structures
These data structures are built from primitive data types like int, float, double, char etc.
Example:- An array is a data structure that holds the same data type and the structure is also a data type that holds different data types.
2. Compound Data Structures
You can also build compound data structures by combining simple data structures. Compound data structures are classified into:-
a. Linear Data Structure:– If the elements of a data structure are ordered in sequence then it is a linear data structure. Example:- stacks, queues and linked lists.
b. Non-Linear Data Structure:– These data structures are not linear. These are multilevel data structures. Example:- trees, graphs etc.
3. Static and Dynamic Data Structures
Static data structures are constant in size and structure. It is associated with specific memory locations fixed at compilation time.
You can expand or contract a data structure according to your needs during the execution of the program. And these types of data structures are known as Dynamic Data Structure.
Operations on Data Structures
Below are the basic operations which you can perform on the data structures in C++:-
- Insertion: Adding a new data element into the data structure.
- Deletion: This operation is about deleting or removing an existing data element from the data structure.
- Traversal: This operation is about processing and displaying all the data elements in the data structure.
- Searching: Searching a specific data element in the data structure.
- Sorting: This operation is about arranging all the data elements in the data structure either in ascending or descending order.
- Merging: This operation is about combining similar data elements from two or more data structures.
C++ Linked List
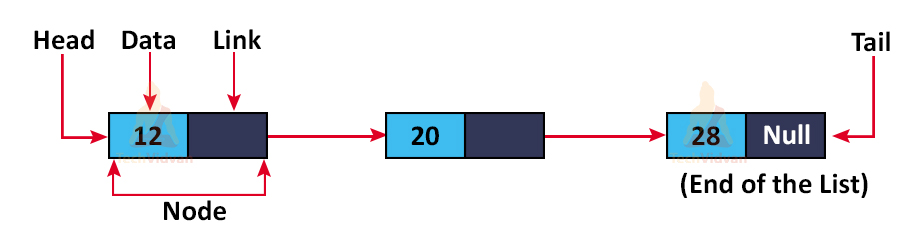
A linked list can be defined as a collection of connected nodes. It is a linear data structure. A linked list contains two parts such as:-
- Data Part:- Contains the data of the user.
- Pointer Part:- It points to the next member of the linked list.
In the above image, Head contains the address of the first node. And the last node in the linked list points to NULL.
Nodes are stored at different locations.
There are three types of linked list such as Singly Linked List, Doubly Linked List and Circular Linked List.
Below, we have created a singly linked list of three members.
// Node Initializing! struct node *HEAD; struct node *ONE = NULL; struct node *TWO = NULL; struct node *THREE = NULL; // Allocating memory! ONE = malloc(sizeof(struct node)); TWO = malloc(sizeof(struct node)); THREE = malloc(sizeof(struct node)); // Assigning the values of data! ONE->data = 23; TWO->data = 34; THREE->data = 90; // Connecting nodes with each other! ONE->next = TWO; TWO->next = THREE; THREE->next = NULL; // Saving the address of first node HEAD = ONE;
Stack in C++
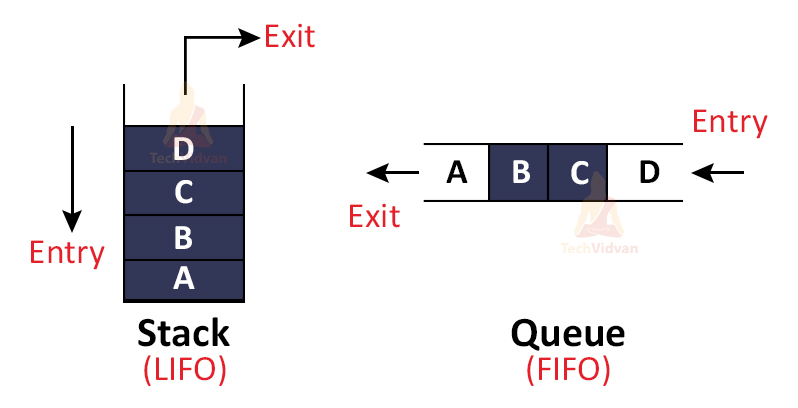
Stack is known as a linear data structure. It follows the Last-In-First-Out rule. So, if you push something to the stack then the last value which you pushed, will be the first to pop out. The insertion and deletion operation on the stack will only take place from one end which is the top of the stack.
In 2 ways, you can implement a stack in C++:-
1. Statically:- You can implement a stack using an array. It allows static memory allocation of its data elements. In this, the stack inherits all the features of the array.
2. Dynamically:- You can also implement a stack using a linked list. It allows dynamic memory allocation of its data elements. In this, the stack takes over the characteristics of the linked list.
Queue in C++
Queue is known as a linear data structure. It follows the First-In-First-Out rule. So, if you push something to the stack then the first value of the stack will pop out. In the queue, the insertion operation is possible from the rear end(back) and the deletion is from the front.
In 2 ways, you can implement the queue:-
1. Statically:- You can implement a queue using an array. It allows static memory allocation of its data elements. In this, the queue inherits all the features of the array.
2. Dynamically:- You can also implement a queue using a linked list. It allows dynamic memory allocation of its data elements. In this, the queue takes over the characteristics of the linked list.
C++ Trees
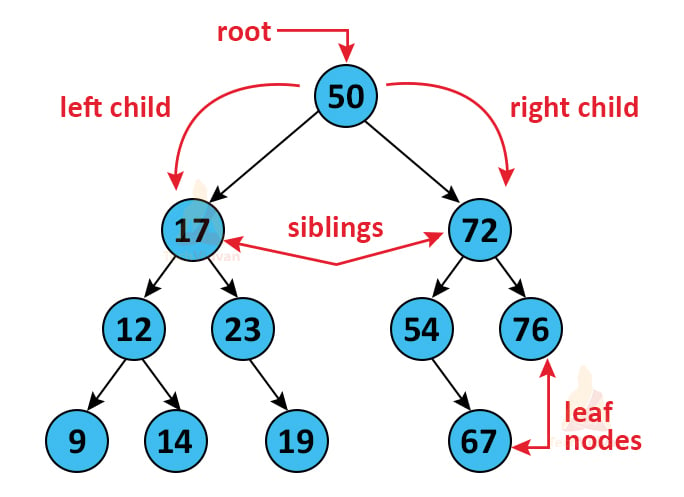
It is a bit of a complex and complicated data structure.
A tree is known as a finite and non-empty set of elements in mathematical terms. Trees are hierarchical data structures. A tree includes multiple nodes. This data structure follows the parent-child relationship. It is not a linear data structure like array, structure, linked lists etc. It is a non-linear data structure.
C++ Arrays
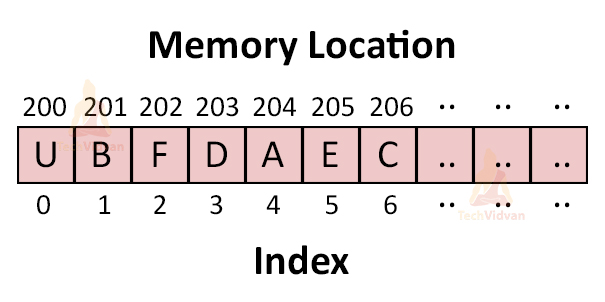
Arrays are simply a collection of similar data types stored at contiguous memory locations. It can store primitive types of data like int, char, float, double etc. With the help of the arrays, a programmer can access the elements very easily.
Suppose, you want to store marks of 20 students then you might try to declare 20 variables like student1_marks, student2_marks etc. But what if i tell you that you can do all those with a single variable named array. With the help of a few lines of code, you can access those elements.
| 6 | 9 | 8 | 5 | 3 |
0 1 2 3 4
Array of size 5
Syntax for declaring an array:-
dataType array_name[arraySize];
So, if you want to access the second element of the above array, then you have to do:-
cout<<array[1]
Example:-
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int numbers[3] = {2, 3, 4};
cout<<"First number is: "<<numbers[0]<<endl;
cout<<"Last number is: "<<numbers[2];
}
Output:-
Last number is: 4
C++ Program Startup and Termination
A C++ program performs the same operations as a C program does at program startup and at program termination, plus a few more outlined here.
Before the target environment calls the function main, and after it stores any constant initial values you specify in all objects that have static duration, the program executes any remaining constructors for such static objects. The order of execution is not specified between translation units, but you can nevertheless assume that some iostreams objects are properly initialized for use by these static constructors. These control text streams are:
cin — for standard input.
cout — for standard output.
cerr — for unbuffered standard error output.
clog — for buffered standard error output.
You can also use these objects within the destructors called for static objects, during program termination.
As with C, returning from main or calling exit calls all functions registered with atexit in reverse order of registry. An exception thrown from such a registered function calls terminate